Equivalence Partitioning Test Case Design Technique
Equivalence Partitioning Test case design technique is one of the testing techniques. You could find other testing techniques such as Boundary Value Analysis, Decision Table and State Transition Techniques by clicking on appropriate links.
Equivalence Partitioning is also known as Equivalence Class Partitioning. In equivalence partitioning, inputs to the software or system are divided into groups that are expected to exhibit similar behavior, so they are likely to be proposed in the same way. Hence selecting one input from each group to design the test cases.
Check below video to see “Equivalence Partitioning In Software Testing”
Each and every condition of particular partition (group) works as same as other. If a condition in a partition is valid, other conditions are valid too. If a condition in a partition is invalid, other conditions are invalid too.
It helps to reduce the total number of test cases from infinite to finite. The selected test cases from these groups ensure coverage of all possible scenarios.
Equivalence partitioning is applicable at all levels of testing.
Example on Equivalence Partitioning Test Case Design Technique:
Example 1:
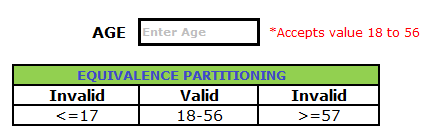
Assume, we have to test a field which accepts Age 18 – 56
Valid Input: 18 – 56
Invalid Input: less than or equal to 17 (<=17), greater than or equal to 57 (>=57)
Valid Class: 18 – 56 = Pick any one input test data from 18 – 56
Invalid Class 1: <=17 = Pick any one input test data less than or equal to 17
Invalid Class 2: >=57 = Pick any one input test data greater than or equal to 57
We have one valid and two invalid conditions here.
Example 2:
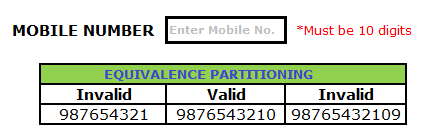
Assume, we have to test a filed which accepts a Mobile Number of ten digits.
Valid input: 10 digits
Invalid Input: 9 digits, 11 digits
Valid Class: Enter 10 digit mobile number = 9876543210
Invalid Class Enter mobile number which has less than 10 digits = 987654321
Invalid Class Enter mobile number which has more than 11 digits = 98765432109



![Software Test Plan Template with Detailed Explanation [Sample Test Plan Document]](https://www.softwaretestingmaterial.com/wp-content/uploads/2015/12/test-plan-template-768x432.png)


You are testing software that controls the amount of water sprayed by an automatic sprinkler
system. The amount to be sprayed in an hour is determined by the weather conditions for the
previous 3 days. The weather conditions can be either sunny, cloudy or rainy. The maximum
amount of water will be sprayed if the previous conditions were sunny, sunny, sunny. No water
will be sprayed if there were two rainy days in the previous three days. Varying amounts will be
sprayed depending on the mix of the previous days. For example, rainy, sunny, sunny will get
more water than sunny, cloudy, rainy.
The software also determines the type of spray to use based on the type of grass being
sprayed. There are five different categories of grasses that are supported.
By applying equivalence partitioning to the weather conditions, how many test cases will be
needed to cover the weather conditions and spray types?
a. 9
b. 15
c. 21
d. 27
Do you have answer for this question, if yes then please give answer with explanation.
Thanks for sharing