Top 40+ Java Interview Questions And Answers in 2025

In this post, we see Core Java Interview Questions for Freshers and Experienced. This post covers Core Java Interview Questions for Selenium Automation Testers too. This post on Java Interview Questions is prepared with basic and important concepts of Java with examples for your easy understanding.
Don’t miss Java Quiz
Related Posts:
Most Frequently asked Java Interview Questions
Let’s move on and see this comprehensive list of the most important and commonly asked basic and advanced Java programming Interview Questions with answers.
1. Explain Java Main Method public static void main (String[] args)
When you start learning Java, the first method you encounter is public static void main(String [] args). The starting point of any Java Program is the main() method. It is one of the important methods of Java. Technically, the main method is the starting point where the Java program starts its execution. JVM always look for this method signature to start running an application. Check this to know detailed explanation.
2. What is Java?
Java is a programming language and computing platform first released by Sun Microsystems in 1995. There are lots of applications and websites that will not work unless you have Java installed, and more are created every day. Java is fast, secure, and reliable. From laptops to datacenters, game consoles to scientific supercomputers, cell phones to the Internet, Java is everywhere!
Java program which prints Hello World!
public class MyClass {
public static void main(String args[]) {
System.out.println("Hello World!");
}
}
3. Mention some features of Java?
Some of the features which play an important role in the popularity of java are as follows:
- Simple: Java is easy to learn. Even though Java is based on C++ , it was developed by eliminating poor programming practices of C++.
- Object-Oriented: Java is an object-oriented programming language. Everything in Java is an Object.
- Portable: Java run time environment uses a bytecode verification process to make sure that code loaded over the network doesn’t violate Java security constraints.
- Platform independent: Java is platform-independent. Java is a write once, run anywhere language. Without any modifications, we can use a program on different platforms.
- Secured: Java is well known for its security. It delivers virus-free systems.
- High Performance: Java enables high performance with the use of JIT (Just-In-Time) compilers
- Multithreaded: Java Multithreaded features allows us to write programs that can perform many tasks simultaneously. The multithreading concept of Java shares a common memory area. It doesn’t occupy memory for each thread.
4. Is Java 100% Object Oriented Language?
Java is not a pure Object Oriented Language because it supports primitive data type such as byte, boolean, char, double, float, int, long, short. These primitive data types are not object oriented. This is the reason why Java is not 100% object-oriented language.
5. What is the difference between Object-oriented programming language and Object-based programming language?
There is a difference between Object Oriented Languages and Object Based languages.
Object Oriented Languages:
- Some of the Object Oriented Languages are Java, C#, VB. Net, Smalltalk etc.,
- These languages support all the concepts of OOPs.
- These languages don’t have the inbuilt objects.
Object Based Languages:
- Some of the Object Based Languages are JavaScript, VBScript etc.,
- These languages support all the concepts of OOPs like inheritance and polymorphism.
- These languages have the inbuilt objects, say JavaScript has window object.
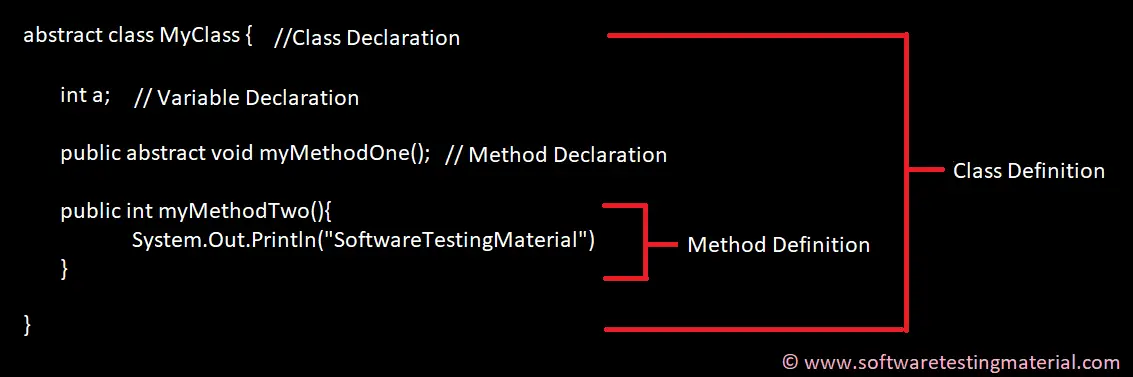
6. What is the difference between Declaration and Definition in Java?
Declaration: If you just declare a class or method/function or variable without mentioning anything about what that class or method/function or variable looks like is called a declaration in Java.
Definition: If you define how a class or method/function or variable is implemented then it is called definition in Java.
When we create an interface or abstract class, we simply declare a method/function but not define it.
For a clear understanding, check the below image
7. What is JRE, and why is it required?
JRE stands for “Java Runtime Environment”. It comprises of the JVM (Java Virtual Machine), Java platform classes, and supporting libraries.
Using JRE, we can only execute already developed applications. We cannot develop new applications or modify existing applications.
As the name suggests, JRE only provides Runtime Environment.
8. What is JDK, and why is it required?
JDK stands for Java Development Kit. It is a superset of JRE (Java Runtime Environment).
Using JDK, we can develop, compile and execute (run) new applications and also we can modify existing applications. We need to install JDK in developers machine where we want to develop new applications or modify existing applications.
JDK includes JRE and development tools (environment to develop, debug and monitor Java programs).
9. What is JVM, and why is it required?
JVM stands for Java Virtual Machine. JVM drives the java code. Using JVM, we can run java byte code by converting them into current OS machine language. It makes Java to become a portable language (write once, run anywhere)
10. What is an Object in Java?
An object is an instance of a class. Objects have state (variables) and behavior (methods).
Example: A dog is an object of Animal class. The dog has its states such as color, name, breed, and behaviors such as barking, eating, wagging her tail.
public class MyClass{ //Class name (MyClass) declaration
public static void main(String[] args){
MyClass obj = new MyClass(); //Object Creation
}
}
11. What is a Class in Java?
A class can be defined as a collection of objects. It is the blueprint or template that describes the state and behavior of an object.
public class MyClass{ //Class name (MyClass) declaration
int a = 9; // Variable declaration
int b = 99;
public void myMethod(){ //Method (myMethod) declaration
int sum=a+b;
}
}
12. What is Constructor in Java?
Constructor in Java is used in the creation of an Object that is an instance of a Class. The constructor name should be the same as the class name. It looks like a method but it’s not a method. It won’t return any value. We have seen that methods may return a value. If there is no constructor in a class, then the compiler automatically creates a default constructor.
13. What is Local Variable and Instance Variable?
Local Variable:
A local variable is a variable that we declare inside a Method. A method will often store its temporary state in local variables.
It can be accessible only inside a block, function, or constructor.
public void website() {
String websiteName;
double websiteLoadTime;
int webisteAge;
}
String websiteName, double websiteLoadTime, int websiteAge are Local variables in above example.
Instance Variable (Non-static):
An instance variable is a variable that is declared inside a Class but outside a Method. We don’t declare this variable as Static because these variables are non-static variables.
It can be accessible by all the methods in the class.
class website() {
public String websiteName;
public double websiteLoadTime;
public int webisteAge;
}
websiteName, websiteLoadTime, websiteAge are Instance variables in above example.
Read more about Variables in Java here
14. What are the OOPs concepts?
OOPS Stands for Object-Oriented Programming System. It includes Abstraction, Encapsulation, Inheritance, Polymorphism, Interface, etc.,
Read more on OOPs concept in Java
15. What is Inheritance in Java?
Inheritance is a process where one class inherits the properties (methods & fields) of another class. Read more here
16. What is Polymorphism?
Polymorphism allows us to perform a task in multiple ways. Let’s break the word Polymorphism and see it, ‘Poly’ means ‘Many’ and ‘Morphos’ means ‘Shapes’. Read more here
Assume we have four students and we asked them to draw a shape. All the four may draw different shapes like Circle, Triangle, and Rectangle.
17. What are the types of Polymorphism?
There are two types of Polymorphism in Java
1. Compile time polymorphism (Static binding) – Method overloading
2. Runtime polymorphism (Dynamic binding) – Method overriding
We can perform polymorphism by ‘Method Overloading’ and ‘Method Overriding’
18. What is Method Overloading?
A class having multiple methods with the same name but different parameters are called Method Overloading
There are three ways to overload a method.
- Parameters with different data types
- Parameters with a different sequence of data types
- Different number of parameters
Read more on Method Overloading in Java
19. What is Method Overriding?
Declaring a method in child class that is already present in the parent class is called Method Overriding.
In simple words, overriding means to override the functionality of an existing method.
In this case, if we call the method with the child class object, then the child class method is called. To call the parent class method we have to use super keyword.
Read more on Method Overriding
20. What is Abstraction in Java?
Abstraction is the methodology of hiding the implementation of internal details and showing the functionality to the users.
Example: Mobile Phone.
A layman who is using a mobile phone doesn’t know how it works internally but he can make phone calls.
21. What is Abstract Class in Java?
We can easily identify whether a class is an abstract class or not. A class that contains abstract keyword in its declaration then it is an Abstract Class.
Syntax:
abstract class <class-name>{}
Points to remember:
- Abstract classes may or may not include abstract methods
- If a class is declared abstract then it cannot be instantiated.
- If a class has abstract method then we have to declare the class as abstract class
- When an abstract class is subclassed, the subclass usually provides implementations for all of the abstract methods in its parent class. However, if it does not, then the subclass must also be declared abstract.
22. What is Abstract Method?
An abstract method is a method that is declared without an implementation (without braces, and followed by a semicolon), like this:
abstract void myMethod();
In order to use an abstract method, you need to override that method in sub class.
23. What is Interface in Java?
An interface in Java looks similar to a class but both the interface and class are two different concepts. An interface can have methods and variables just like the class but the methods declared in interface are by default abstract. We can achieve 100% abstraction and multiple inheritance in Java with Interface. Read more on Interface in Java.
24. What is Encapsulation in Java?
Encapsulation is a mechanism of binding code and data together in a single unit. Let’s take an example of Capsule. Different powdered or liquid medicines are encapsulated inside a capsule. Likewise in encapsulation, all the methods and variables are wrapped together in a single class. Read more on Encapsulation in Java
25. What is String in Java?
String in Java is an object that represents sequence of characters. An array of characters works same as Java string. String in Java is an immutable (cannot grow) object that means it is constant and cannot be changed once it is created.
For example:
char[] c={‘S’,’T’,’M’};
26. Why are strings immutable in Java?
In Java, String is immutable to make sure that the string value doesn’t change. String literals are usually shared between multiple clients. If the value of the string changes (from “STM” to “stm”), it will affect all reference variables and cause severe discrepancies.
Hence, strings are immutable in Java. Making string immutable enhances security, caching, synchronization, and performance of the application.
27. What is the difference between equals() method and double equal operator (==) in Java?
equals() method
- This method is defined in the Object class in Java.
- It is used for checking the equality of contents between two objects defined by business logic.
- public boolean equals(Object o) is the method provided by the Object class.
double equal operator (==)
- It is a binary operator in Java.
- It is used for comparing addresses (or references), i.e checks if both the objects are pointing to the same memory location.
- Default implementation uses double equal operator == to compare two objects.
28. How to convert Integer to String in Java?
package softwareTestingMaterial;
public class STM {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int x = 123;
int y = 456;
String s1 = Integer.toString(x);
String s2 = Integer.toString(y);
System.out.println(""String s1 = "" + s1);
System.out.println(""String s2 = "" + s2);
}
}
29. How to convert String to Integer in Java?
package softwareTestingMaterial;
public class STM {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str = ""100"";
// Integer.parseInt()
System.out.println( Integer.parseInt( str ));
}
}
30. How to convert Char to Integer in Java?
package softwareTestingMaterial;
public class STM {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Initializing a character(ch)
char c = '9';
// Converting the character to an interger value
int number = Integer.parseInt(String.valueOf(c));
System.out.println(number);
}
}
31. Write a program to print the pattern given below
1 1 2 1 2 3 1 2 3 4 1 2 3 4 5
Here is the program to print the pattern mentioned above
package softwareTestingMaterial;
public class NumberPattern {
public static void main(String[] args) {
for (int x = 1; x <= 5; x++) {
for (int y = 1; y <= x; y++) {
System.out.print(y+" ");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
}
32. Write a program to print the pattern given below (Left Triangle Star Pattern)
* * * * * * * * * * * * * * *
Here is the program to print the pattern mentioned above
package softwareTestingMaterial;
public static void main(String args[])
{
//x for rows, y for columns, and row denotes the number of rows to print
int x, y, row=5;
//outer loop for rows
for(x=0; x<row; x++)
{
//inner loop for columns
for(y=0; y<=x; y++)
{
//To prints stars
System.out.print("* ");
}
//Cursor goes to the new line after printing each line.
System.out.println();
}
}
}
33. Write a program to print the pattern given below (Right Triangle Star Pattern)
*
* *
* * *
* * * *
* * * * *
Here is the program to print the pattern mentioned above
package softwareTestingMaterial;
public static void main(String args[])
{
//x for rows, y for columns, and row denotes the number of rows to print
int x, y, row=5;
//outer loop for number of rows
for(x=0; x<row; x++)
{
//inner loop for columns
for(y=2*(row-x); y>=0; y--)
{
//To prints spaces
System.out.print(" ");
}
//Inner loop for columns
for(y=0; y<=x; y++)
{
//To prints stars
System.out.print("* ");
}
//Cursor goes to the new line after printing each line
System.out.println();
}
}
}
34. Write a program to print the pattern given below (Pyramid Star Pattern)
* * * * * * * * * * * * * * *
Here is the program to print the pattern mentioned above
public static void main(String args[])
{
//x for rows, y for columns, and row denotes the number of rows to print
int x, y, row = 5;
//Outer loop for rows
for (x=0; x<row; x++)
{
//inner loop for space
for (y=row-x; y>1; y--)
{
//To print space between two stars
System.out.print(" ");
}
//inner loop for columns
for (y=0; y<=x; y++ )
{
//To print star
System.out.print("* ");
}
//Cursor goes to the new line after printing each line.
System.out.println();
}
}
35. Write a program to print Fibonacci Series up to count 10.
package softwareTestingMaterial;
public class FibonacciSeries {
public static void main(String args[]) {
int a = 0, b = 1, c, i, count = 10;
// To print 0 and 1
System.out.print(a + " " + b);
// loop starts from 2. We have already printed 0 and 1 in the previous step
for (i = 2; i < count; i++) {
c = a + b;
System.out.print(" " + c);
a = b;
b = c;
}
}
}
36. How to reverse a String in Java?
package softwareTestingMaterial;
public class ReverseString {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Using StringBuffer class
StringBuffer a = new StringBuffer("Software Testing Material");
// use reverse() method to reverse string
System.out.println(a.reverse());
}
}
Another method:
package softwareTestingMaterial;
public class ReverseString {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String input="Software Testing Material";
StringBuilder input1 = new StringBuilder();
input1.append(input);
input1=input1.reverse();
for (int i=0;i<input1.length();i++)
System.out.print(input1.charAt(i));
}
}
Check this for other methods we use to reverse a String in Java
37. How To Find The Largest Value From The Given Array.
package softwareTestingMaterial;
public class LargestValue {
public static void main(String[] args){
int[] arr={28,3,15,9,17,4,23,2};
int val=arr[0];
for(int i=0; i<arr.length; i++){
if(arr[i] > val){
val=arr[i];
}
}
System.out.println("Largest value in the Given Array is "+ val);
}
}
38. How to display all the prime numbers between 1 and 100
The number which is only divisible by 1 and itself is known as a prime number. For example 2, 3, 5, 7, 11… are prime numbers.
package softwareTestingMaterial;
public class PrimeNumbersOneToHundred {
public static void main (String[] args){
int i =0;
int num =0;
String primeNumbers = "";
for (i = 1; i <= 100; i++){
int counter=0;
for(num =i; num>=1; num--){
if(i%num==0){
counter = counter + 1;
}
}
if (counter ==2){
primeNumbers = primeNumbers + i + " ";
}
}
System.out.println("Prime numbers from 1 to 100 are :");
System.out.println(primeNumbers);
}
}
39. How to display all the prime numbers between 1 and n (n is the number, get the input from user)
package softwareTestingMaterial;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class PrimeNumbersOneToN {
public static void main (String[] args){
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
int i =0;
int num =0;
String primeNumbers = "";
System.out.println("Enter the value of n :");
int n = scanner.nextInt();
scanner.close();
for (i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
int counter=0;
for(num =i; num>=1; num--)
{
if(i%num==0)
{
counter = counter + 1;
}
}
if (counter ==2)
{
primeNumbers = primeNumbers + i + " ";
}
}
System.out.println("Prime numbers from 1 to n are :");
System.out.println(primeNumbers);
}
}
40. How to find the given number is a prime number or not by getting input from the user
package softwareTestingMaterial;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class PrimeNumberVerification {
public static void main(String args[])
{
int i, j, flag = 0;
System.out.print("Enter any number which you want to verify whether it is a prime number or not :");
Scanner s = new Scanner(System.in);
j = s.nextInt();
for( i = 2; i < j; i++){
if(j % i == 0){
flag = 0;
break;
}
else
{
flag = 1;
}
}
if(flag == 1){
System.out.println(j+" is a prime number.");
}
else{
System.out.println(+j+" is not a prime number.");
}
}
}
41. Write a program to print Fibonacci Series
Method 1:
package softwareTestingMaterial;
public class FibonacciSeries {
public static void main(String args[]) {
int a = 0, b = 1, c, i, count = 10;
// To print 0 and 1
System.out.print(a + " " + b);
// loop starts from 2. We have already printed 0 and 1 in the previous step
for (i = 2; i < count; i++) {
c = a + b;
System.out.print(" " + c);
a = b;
b = c;
}
}
}
Method 2:
package softwareTestingMaterial;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class FibonacciSeriesOne {
public static void main(String[] args){
System.out.println("Enter Iteration to print Fibonacci Series");
FibonacciCheck.checkFibonacci(new Scanner(System.in).nextInt());
}
}
class FibonacciCheck {
public static void checkFibonacci(int number){
int first=0,second=1;
int third=0;
int i=1;
System.out.print("Fibonacci Series upto: "+number+" is ");
System.out.print(first+","+second+",");
while(i<=number){
third=first+second;
System.out.print(third+",");
first=second;
second=third;
++i;
}
}
}
42. How to read a file line by line in Java?
We can read a file line by line in Java in two ways.
1. BufferedReader Class
2. Scanner Class
Using BufferedReader Class:
BufferedReader Class belongs to java.io package and it provides readLine() method to read a file line by line in Java.
package softwareTestingMaterial;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.FileReader;
import java.io.IOException;
public class ReadLineByProgram {
public static void main(String[] args) {
BufferedReader reader;
try {
reader = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(
"/Users/Rajkumar/Downloads/STM.txt"));
String line = reader.readLine();
while (line != null) {
System.out.println(line);
// read next line
line = reader.readLine();
}
reader.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
Using Scanner Class:
Java Scanner class provides the nextLine() method to facilitates line by line of file’s content.
package softwareTestingMaterial;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class ReadLineByProgram {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(new File("/Users/Rajkumar/Downloads/STM.txt"));
while (scanner.hasNextLine()) {
System.out.println(scanner.nextLine());
}
scanner.close();
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
43. Difference between Array and ArrayList?
| Array | ArrayList |
|---|---|
| Array is static | ArrayList is dynamic |
| Size of the array should be given at the time of array declaration. We cannot change the size of array after creating it | Size of the array may not be required. It changest the size dynamically. Capacity of ArrayList increases automatically whenever we add elements to an ArrayList |
| Array can contain both primitive data types as well as objects | ArrayList cannot contain primitive data types. It contains only objects |
| Arrays are multidimensional | ArrayList is always single dimension |
44. Difference between ArrayList and HashSet in Java?
| ArrayList | HashSet |
|---|---|
| ArrayList implements List interface | HashSet implements Set interface |
| ArrayList allows duplicates | HashSet doesn’t allow duplicates |
| ArrayList is an ordered collection and maintains insertion order of elements | HashSet is an unordered collection and doesn’t maintain insertion order |
| ArrayList is backed by an Array | HashSet is backed by an HashMap instance |
| ArrayList is an index based | HashSet is object based |
| In ArrayList, we can retrive object by calling get() method or remove object by calling remove() method | In HashSet, we can’t achieve get() method |
Learn more on Array and ArrayList with sample programs
45. What are the different access modifiers available in Java?
Access modifiers are subdivided into four types such as Default, Public, Private, Protected
default: The scope of default access modifier is limited to the package only. If we do not mention any access modifier, then it acts like a default access modifier.
private: The scope of private access modifier is only within the classes.
Note: Class or Interface cannot be declared as private
protected: The scope of protected access modifier is within a package and also outside the package through inheritance only.
Note: Class cannot be declared as protected
public: The scope of public access modifier is everywhere. It has no restrictions. Data members, methods and classes that declared public can be accessed from anywhere.
See some sample programs of access modifiers
46. Difference between static binding and dynamic binding?
1. Static binding is also known as early binding whereas dynamic binding is also known as late binding.
2. Determining the type of an object at compile time is Static binding whereas determining the type of an object at run time is dynamic binding
3. Java uses static binding for overloaded methods and dynamic binding for overridden methods.
To know more about this you have to go through Method Overloading and Method Overriding.
47. Difference between Abstract Class and Interface?
| ABSTRACT CLASS | INTERFACE |
|---|---|
| To declare Abstract class we have to use abstract keyword | To declare Interface we have to use interface keyword |
| In an Abstract class keyword abstract is mandatory to declare a method as an abstract | In an Interface keyword abstract is optional to declare a method as an abstract. Compiler treats all the methods as abstract by default |
| An abstract class contains both abstract methods and concrete methods(method with body) | An interface can have only abstract methods |
| An abstract class provides partial abstraction | An interface provides fully abstraction |
| An abstract class can have public and protected abstract methods | An interface can have only public abstract methods |
| An abstract class can have static, final or static final variables with any access modifiers | An interface can have only public static final variables |
| An abstract class can extend one class or one abstract class | An interface can extend any number of interfaces |
| Abstract class doesn't support multiple inheritance | Interface supports multiple inheritance |
48. What is Multiple Inheritance?
If a class implements multiple interfaces, or an interface extends multiple interfaces then it is known as multiple inheritance.
49. What are the differences between throw and throws in Java?
throw keyword
- The throw keyword is used to explicitly throw an exception in the program inside a function or inside a block of code.
- The checked exceptions cannot be propagated with throw only.
- The throw keyword is followed by an instance.
- The throw keyword is used within the method.
- You cannot throw multiple exceptions.
throws keyword
- The throws keyword is used in the method signature to declare an exception which might get thrown by the function while executing the code.
- The checked exception can be propagated with throws
- The throws keyword is followed by class.
- The throws keyword is used with the method signature.
- You can declare multiple exceptions, e.g., public void method()throws IOException, SQLException.
We will update this post “Java Interview Questions For Selenium Testers” ASAP. Keep visiting.
If you like this post, share it with your friends.
Learn Java with Sample Programs
Related Posts:
- Selenium Interview Questions
- Test Automation Framework Interview Questions
- How To Explain Test Automation Framework In The Interview
- Why Did You Choose Software Testing As Your Career
- Tell Me About Yourself
- What Are Your Strengths










hi,
Rajkumar Sir i want to know more about related to selenium and more questions on java related to selenium will you plz provide more questions on java
Hi Deosur Umesh, Sure I will update ASAP. Also I will publish Java tutorial by end of this weekend.
Hi team,
Please post a interview question and answer on java 8 .
Hi Rajkumar,
Could you please update the interview question for selenium and java..
Thanks
Anmol j k
Hi Anmol, Sure we will do it ASAP.
Please double check answer to 25th question.
Hi Hema, Good catch. It has been updated.